 A federal judge formally refused on Tuesday to let the Pentagon reinstate its ban on openly gay men and women in the U.S. military while it appeals her decision declaring its "don't ask, don't tell" policy unconstitutional.
A federal judge formally refused on Tuesday to let the Pentagon reinstate its ban on openly gay men and women in the U.S. military while it appeals her decision declaring its "don't ask, don't tell" policy unconstitutional.
A day after tentatively siding against the Obama administration, U.S. District Judge Virginia Phillips issued a written decision denying a government request to lift her own injunction barring further Pentagon enforcement of the ban.
Judge affirms order opening military to gays
5 times we almost nuked ourselves by accident
 We spent the Cold War in perpetual fear that the U.S. and U.S.S.R. would start an intentional nuclear conflict. The truth is, we came far closer to blowing ourselves up with nuclear weapons than we ever came to WWIII.
We spent the Cold War in perpetual fear that the U.S. and U.S.S.R. would start an intentional nuclear conflict. The truth is, we came far closer to blowing ourselves up with nuclear weapons than we ever came to WWIII.
Nuclear incidents have a bunch of ominous military code names, like Broken Arrow, Faded Giant or NUCFLASH. There are actually dozens of instances like these, but here are five major ones that happened in the U.S. If we were to consider Soviet activity, the list could go on for hours. The Russians either lost a nuclear sub, lost a sub with nuclear weapons on board, had a nuclear sub's reactor melt down, or all three roughly every other week. Kompetentnyh? Nyet.
Soldier silenced for testimony in Afghan killings probe
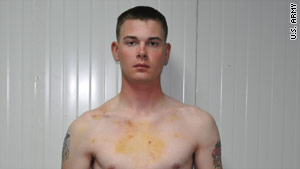 First, Justin Stoner blew the whistle on his platoon. Now, the Army apparently wants to silence him. In photos obtained by CNN, Stoner sports bruises and abrasions on his back, chest and near his neck -- the marks of a beating inflicted by fellow soldiers as payback for reporting their rampant hashish use, the Army said.
First, Justin Stoner blew the whistle on his platoon. Now, the Army apparently wants to silence him. In photos obtained by CNN, Stoner sports bruises and abrasions on his back, chest and near his neck -- the marks of a beating inflicted by fellow soldiers as payback for reporting their rampant hashish use, the Army said.
At the time, those close to the investigation tell CNN, Stoner just wanted the smoking in his tent and around him to stop. So he went outside his group and reported the drug use to his superiors.
Are We Giving Our Soldiers Drugs That May Make Them Kill Themselves?

More troops are dying by their own hand than in combat, according to an Army report titled "Health Promotion, Risk Reduction, Suicide Prevention." Not only that, but 36 percent of the suicides were troops who were never deployed.
California National Guard bonus program riddled with corruption
 Master Sgt. Toni Jaffe was known as "the M&M lady" because she decorated her office cubicle with keepsakes of the confection's advertising characters. However, the treats she dispensed were sweeter than candy and are now the subject of a criminal investigation.
Master Sgt. Toni Jaffe was known as "the M&M lady" because she decorated her office cubicle with keepsakes of the confection's advertising characters. However, the treats she dispensed were sweeter than candy and are now the subject of a criminal investigation.
From 1986 until her retirement last year, Jaffe's job with the California Army National Guard was to give away money — the federally subsidized student-loan repayments and cash bonuses — paid for by federal taxpayers nationwide — that the Guard is supposed to use to attract new recruits and encourage Guard members to reenlist.
Broken Promises: Thousands of Veterans Denied Crucial Care
 The Army tacked a five-month extension on Sgt. Ryan Christian Major's term of military service in 2006, and that November, just five days after his original discharge date, Ryan was critically injured when an underground bomb exploded during a foot patrol in Ramadi, Iraq.
The Army tacked a five-month extension on Sgt. Ryan Christian Major's term of military service in 2006, and that November, just five days after his original discharge date, Ryan was critically injured when an underground bomb exploded during a foot patrol in Ramadi, Iraq.
Ryan was evacuated from Iraq and brought to a hospital in Germany, where he underwent extensive surgery. His pelvis had been broken, and doctors amputated both of his legs above the knees. He suffered from traumatic brain injury (TBI) and would go on to develop post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). For two months after the explosion, Ryan's family was unsure of he would survive. He did.
Blackwater Wins Piece of $10 Billion Mercenary Deal
 Never mind the dead civilians. Forget about the stolen guns. Get over the murder arrests, the fraud allegations, and the accusations of guards pumping themselves up with steroids and cocaine. Through a “joint venture,” the notorious private-security firm Blackwater has won a piece of a five-year State Department contract worth up to $10 billion, Danger Room has learned.
Never mind the dead civilians. Forget about the stolen guns. Get over the murder arrests, the fraud allegations, and the accusations of guards pumping themselves up with steroids and cocaine. Through a “joint venture,” the notorious private-security firm Blackwater has won a piece of a five-year State Department contract worth up to $10 billion, Danger Room has learned.
More Articles...
Page 60 of 99

 Military Glance
Military Glance






























